T-I-3draft: Difference between revisions
Frmignacco (talk | contribs) |
Frmignacco (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Definition of Radon transform == | == Definition of Radon transform == | ||
=== Definition: === | === Definition: === The Radon transform of a function <math> f : \mathbb{R}^2\rightarrow \mathbb{R}</math> is the function <math>\hat f : \mathbb{R}^2\rightarrow \mathbb{R}</math> defined by the following expression | ||
<center><math> | |||
\hat f (t,\textbf{u_t})=\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty}f(t\textbf{u_t}+s\textbf{u_s})\,\textrm{d}s. | |||
</math></center> | |||
=== Use of the <math>\delta-</math>distribution: === The definition of Radon transform can be elegantly written by means of the Dirac-delta distribution. This formulation provides the advantage of generalising the definition of Radon transform to arbitrary dimension. | |||
''' ''' | |||
Revision as of 21:56, 15 October 2021
Radon transform and X-ray tomography
The goal of this homework is to introduce the Radon transform of a two-dimensional function. We will show that this transform is invertible and the inverse involves the Fourier transform in two dimensions. From a practical point of view, the Radon transform is the basis of X-ray tomography (as well as X-ray scanning), applied in the medical context in order to obtain cross-section images of different organs. The second part of the homework consists of a documentation work to be conducted in pairs: each pair of students should prepare a blackboard presentation of approximately five minutes on this part.
Radon transform
Preliminaries: parametrisation of a line in the plane
Q1: In a two-dimensional space, how many parameters are needed in order to define a line? Provide some examples of equations that define a unique line in the plane.
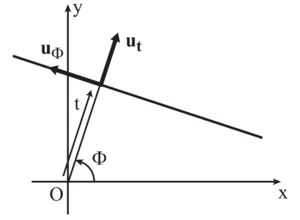
Q2: In the context of Radon transform, we choose to define a line via the parameters and , where , displayed in Figure 1. Each angle is associated to a unique unit vector :
Show that for each given line there exist two possible pairs of values .
Q3: We choose to orient the line positively along the unit vector , defined by:
Show that for each pair there exists a unique oriented line.
Q4: A natural pair of coordinates, associated to the family of lines obtained from a given , is the pair of coordinates of a point in the basis related to the line that passes through that point. Provide the expression for as a function of , as well as the expression for as a function of . Deduce the relation between the surface elements and .
Definition of Radon transform
=== Definition: === The Radon transform of a function is the function defined by the following expression
=== Use of the distribution: === The definition of Radon transform can be elegantly written by means of the Dirac-delta distribution. This formulation provides the advantage of generalising the definition of Radon transform to arbitrary dimension.